What are Power Electronic Converters?
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial control systems, one crucial component that plays a pivotal role in regulating and managing electrical power is the power electronic converter. Power electronic converters are devices that have revolutionized the way electricity is controlled, converted, and distributed in a wide range of applications across various industries. From renewable energy sources to electric vehicles and manufacturing processes, power electronic converters have become indispensable in modern industrial control systems. In this article, we will delve into the world of power electronic converters, exploring their fundamental principles, applications, and their significance in the industrial control field.
Understanding Power Electronic Converters
Power electronic converters are electronic devices designed to efficiently control and manipulate electrical energy. These devices can change the voltage, current, and frequency of electrical power to match the requirements of specific applications. The fundamental principle behind power electronic converters lies in the use of semiconductor devices like diodes, transistors, and thyristors to switch and control the flow of electricity.
Types of Power Electronic Converters
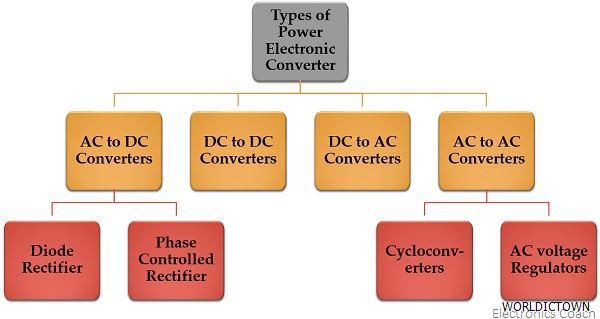
There are several types of power electronic converters, each designed for specific applications. Here are some common types:
Rectifiers: Rectifiers convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). They are commonly used in power supplies for various electronic devices and are essential in industrial applications to ensure a stable and regulated DC power source.
Inverters: Inverters perform the opposite function of rectifiers, converting DC into AC. They are crucial in applications like renewable energy systems, where DC power from solar panels or batteries needs to be converted into AC for use in homes and industries.
DC-DC Converters: These converters change the voltage level of DC power. They are commonly used in electronic devices like laptops and mobile phones to ensure the proper voltage is supplied to the components.
AC-DC Converters: These converters transform AC power into DC power. They are commonly used in power supplies and battery chargers.
AC-AC Converters: AC-AC converters, also known as cycloconverters or frequency converters, can change the frequency, voltage, or phase of AC power. They are used in applications such as motor drives and induction heating.
Applications of Power Electronic Converters
Power electronic converters find applications in a wide range of industrial control systems and beyond. Some of their prominent uses include:
Renewable Energy: In the renewable energy sector, power electronic converters play a crucial role in efficiently converting energy from sources like solar panels and wind turbines into usable electricity for the grid.
Electric Vehicles: Power electronic converters enable the control of energy flow in electric vehicles. They convert DC power from batteries to AC power for the motor and vice versa during regenerative braking.
Manufacturing and Robotics: In manufacturing processes, power electronic converters regulate the operation of machines, ensuring efficient and precise control in various industrial applications.
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): Power converters are a key component in UPS systems, ensuring a seamless transition from the grid to battery power in the event of a power outage.
HVAC Systems: Power converters are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to control the speed of motors, resulting in energy savings.
Significance in the Industrial Control Field
Power electronic converters have transformed the industrial control field by offering enhanced control, increased efficiency, and improved reliability in various applications. Their significance can be summarized as follows:
Energy Efficiency: Power converters enable the precise control of energy flow, reducing energy wastage and enhancing the overall efficiency of industrial processes.
Grid Integration: In the context of renewable energy sources, power electronic converters play a crucial role in integrating these intermittent energy sources into the power grid, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels.
Flexibility and Precision: Power converters offer the flexibility to adapt power output to varying load demands, ensuring stable and reliable power supply for industrial processes.
Reliability and Redundancy: In critical applications like UPS systems, power converters ensure a smooth transition between power sources, minimizing downtime and preventing data loss.
Conclusion
Power electronic converters have become a linchpin in the industrial control field, driving innovation and efficiency in a wide range of applications. As technology continues to advance, power electronic converters will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of industrial processes and energy systems. Their ability to convert and control electrical energy with precision and efficiency makes them an indispensable component of modern industrial control systems, contributing to a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.
Subscribe to Us !
-
 LV71081E-MPB-E
LV71081E-MPB-Eonsemi
-
 LMK00334RTVRQ1
LMK00334RTVRQ1Texas Instruments
-
 PI6C557-03LEX
PI6C557-03LEXDiodes Incorporated
-
 PCM1753DBQR
PCM1753DBQRTexas Instruments
-
 ADS1204IRHBT
ADS1204IRHBTTexas Instruments
-
 MCP4018T-104E/LT
MCP4018T-104E/LTMicrochip Technology
-
 T4F49C2
T4F49C2Efinix, Inc.
-
.jpg) A40MX02-PLG44
A40MX02-PLG44Microchip Technology
-
 ATF16V8C-7PU
ATF16V8C-7PUMicrochip Technology
-
 SC-13048Q-A
SC-13048Q-AGHI Electronics, LLC

